Left Anterior Descending Coronary Artery Ligation (LAD)
Coronary heart disease accounts for about two-thirds of heart failure cases which are often secondary to myocardial infarction(MI). Despite continued progress in heart failure understanding and management, its incidence and prevalence are steadily increasing for many reasons. Murine models of myocardial infarction and ischemia are essential for the investigation of the acute and chronic effects of myocardial ischemia.
Our core provides a reliable and repeatable method for left anterior descending artery (LAD) ligation in mice. This model can be used to study both acute cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury and chronic cardiac ischemia(MI). Factors such as gender, strain and age of the mice also significantly contribute to the pathophysiology of the induced disorder.
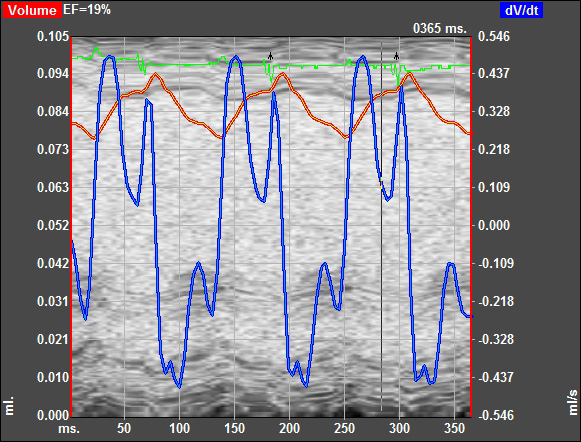
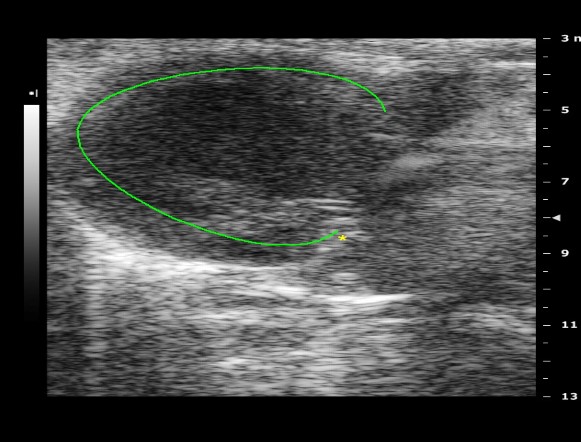
Quantification of MI:
- VisualSonics Vivo 2100 imaging System cardiac echo
- Micron-scale computed tomography (Micro CT/Micro PET)
- Troponin assays
- Histological analysis
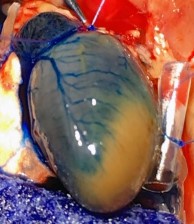
LAD Reperfusion Model: 30 Minute Ischemia with 2 Hour Reperfusion
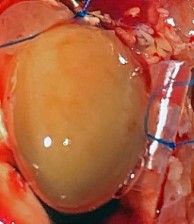
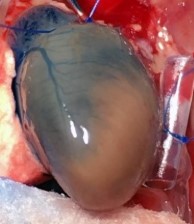
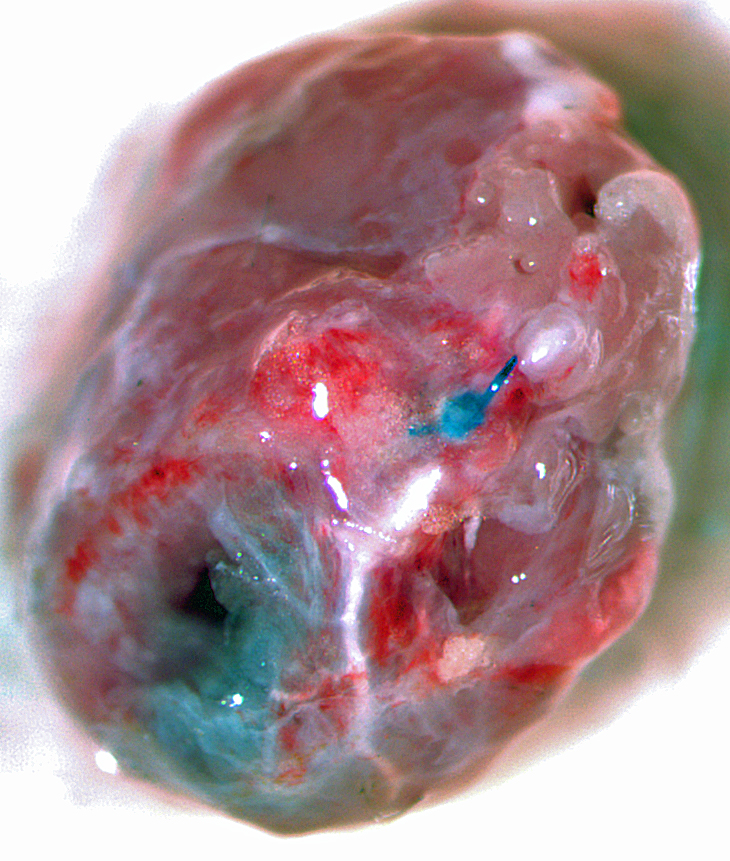
Pictured: Cardiac Perfusion With Evans Blue Dye To Define Infarct zone.
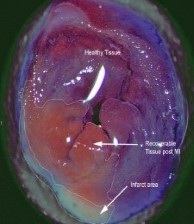
Chronic Ischemia (MI)
4-7 Days Post MI Average 30% Infarct Area. Model Developing Athero
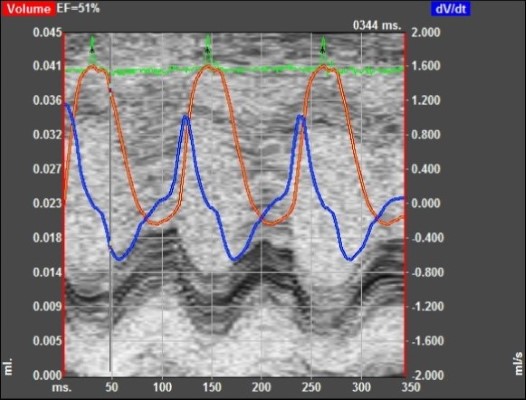
Normal Day-0 Preoperative Baseline Echo Data
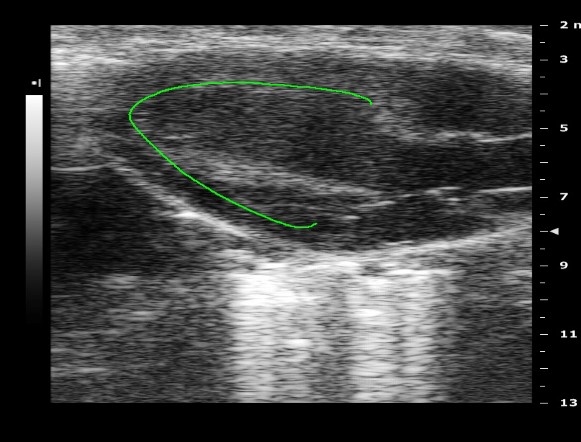
Day-14 Post operative Chronic MI