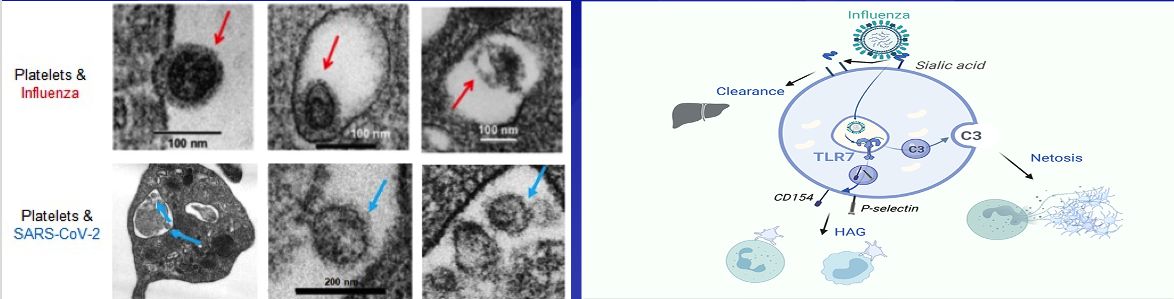
Platelets and Respiratory Viruses
Mechanisms of recognizing and sensing respiratory viruses in platelets
Platelets are central in mediating hemostasis and thrombosis and have also been recognized for mediating an immune response during infection with various pathogens. Human platelets internalize respiratory viruses such as influenza and SARS-CoV-2, they do not get infected, but do become activated. Utilizing blood from human donors and various murine models, research in our lab aims to understand the molecular mechanisms by which platelets internalize respiratory viruses and become activated. A central theme is focused on the description of pathogen-associated molecular pattern receptors and signaling cascades that underlie the immune response to infection and how this response can contribute to immunothrombosis.