MicroRNA Biogenesis
Discovered the Microprocessor and characterized its regulation.
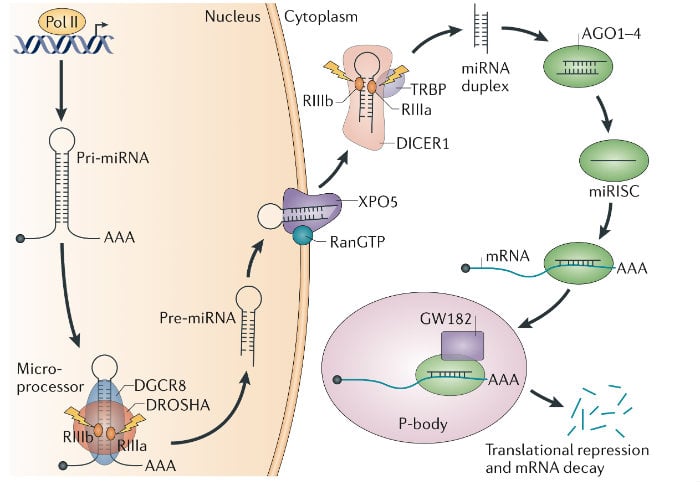
For over a decade my work has focused on uncovering the mechanisms of microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis. As a postdoctoral fellow I identified the ‘Microprocessor’ complex that comprises DROSHA and the double-stranded RNA-binding protein DGCR8. DGCR8 maps to a chromosomal region whose monoallelic deletion causes DiGeorge syndrome, the most common human genetic deletion syndrome. Mouse models subsequently revealed that DGCR8 haploinsufficiency contributes to the neuronal and behavioral phenotypes of this disorder. We later uncovered a feedback mechanism for the precise control of DGCR8 expression. We also discovered that YAP, the downstream target of the tumor-suppressive Hippo-signaling pathway regulates Microprocessor activity in a cell-density dependent manner. This finding provides a mechanistic explanation for two previously reported phenomena — that cell confluence leads to widespread upregulation of miRNAs, and that tumor cells have a generally lower level of miRNA expression than corresponding normal tissue.
- Gregory R. I.*, Yan K.*, Amuthan G., Chendrimada T., Doratotaj B., Cooch N., and Shiekhattar R. The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature 2004, 432, 235-240. PMID: 15531877 (* equal contribution).
- Gregory R. I., Chendrimada T., Cooch N., and Shiekhattar R. Human RISC couples microRNA biogenesis and posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell 2005, 123, 631-40. PMID: 16271387.
- Triboulet R., Chang H., LaPierre R. J., and Gregory R. I. Posttranscriptional control of DGCR8 expression by the Microprocessor. RNA 2009, 15, 1005-11. PMID: 19383765. PMC2685516.
- Mori, M., Triboulet, R., Mohseni, M., Schlegelmilc, K., Shrestha, K., Camargo, F. D., and Gregory, R. I. Hippo signaling regulates Microprocessor and links cell density-dependent miRNA biogenesis to cancer. Cell 2014, 156, 893-906. PMID: 24581491. PMC3982296.