DIS3L2 Mediated Decay
Identified a novel RNA decay pathway in stem cells and cancer.
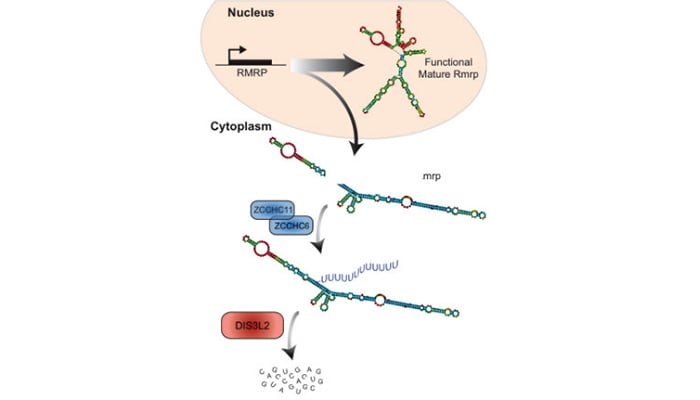 Based on our original discovery that LIN28 selectively controls let-7 expression we sought to better understand the mechanism by which this occurs. This led to our identification that the Terminal Uridylyl Transferase (TUTase), TUT4 (also known as ZCCHC11) is responsible for LIN28-mediated pre-let-7 uridylation and subsequent blockade of let-7 processing. LIN28-binding to pre-let-7 recruits TUT4 and a related TUTase (TUT7/ZCCHC6) to catalyze pre-let-7 uridylation. Significantly, this discovery provides the first demonstration that a TUTase can control miRNA biogenesis. We identified DIS3L2 as the 3'-5' exonuclease responsible for the decay of uridylated pre-let-7 in mouse ESCs. Our paradigm-shifting findings that RNA uridylation triggers degradation by DIS3L2 highlight an important new regulatory mechanism controlling RNA metabolism. Our study also identifies the first physiological RNA substrate of this newly discovered exonuclease, which is mutated in the Perlman syndrome of fetal overgrowth and causes a predisposition to Wilms tumor development. Most recently we applied an unbiased RNA immunoprecipitation strategy to identify Dis3l2 targets in mouse embryonic stem cells. We identified Dis3l2-mediated decay (DMD) as a surveillance pathway for a specific subset of ncRNAs.
Based on our original discovery that LIN28 selectively controls let-7 expression we sought to better understand the mechanism by which this occurs. This led to our identification that the Terminal Uridylyl Transferase (TUTase), TUT4 (also known as ZCCHC11) is responsible for LIN28-mediated pre-let-7 uridylation and subsequent blockade of let-7 processing. LIN28-binding to pre-let-7 recruits TUT4 and a related TUTase (TUT7/ZCCHC6) to catalyze pre-let-7 uridylation. Significantly, this discovery provides the first demonstration that a TUTase can control miRNA biogenesis. We identified DIS3L2 as the 3'-5' exonuclease responsible for the decay of uridylated pre-let-7 in mouse ESCs. Our paradigm-shifting findings that RNA uridylation triggers degradation by DIS3L2 highlight an important new regulatory mechanism controlling RNA metabolism. Our study also identifies the first physiological RNA substrate of this newly discovered exonuclease, which is mutated in the Perlman syndrome of fetal overgrowth and causes a predisposition to Wilms tumor development. Most recently we applied an unbiased RNA immunoprecipitation strategy to identify Dis3l2 targets in mouse embryonic stem cells. We identified Dis3l2-mediated decay (DMD) as a surveillance pathway for a specific subset of ncRNAs.
- Hagan J. P., Piskounova E., and Gregory R. I. Lin28 recruits the TUTase Zcchc11 to inhibit let-7 maturation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2009, 16, 1021-5. PMID: 19713958. PMC2758923.
- Thornton J. E., Chang H., Piskounova E., and Gregory R. I. Lin28-mediated control of let-7 microRNA expression by alternative TUTases Zcchc11 (TUT4) and Zcchc6 (TUT7). RNA 2012, 18, 1875-85. PMID: 22898984. PMC3446710.
- Chang H-M., Triboulet R., Thornton J. E., and Gregory R. I. A role for the Perlman syndrome exonuclease Dis3l2 in the Lin28-let-7 pathway. Nature 2013, 497, 244-8. PMID: 23594738. PMC3651781
- Pirouz M., Du P., Munafò M., and Gregory R. I. Dis3l2-mediated decay is a quality control pathway for noncoding RNAs. Cell Reports 2016, 16, 1861-73. PMID: 27498873. PMC4998061.
- Pirouz M., Ebrahimi A. G., and Gregory R. I. Unraveling 3′-end RNA uridylation at nucleotide resolution. Methods 2019, 155, 10–19. PMID: 30395968. PMC6387850.
- Pirouz M., Munafò M., Ebrahimi A. G., Choe J., and Gregory R. I. Exonuclease requirements for mammalian ribosomal RNA biogenesis and surveillance. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2019, 26, 490–500. PMID: 31160785. PMC6554070.
-
Pirouz M., Wang C. H., Liu Q., Ebrahimi A. G., Shamsi F., Tseng Y-H., Gregory R. I. The Perlman syndrome DIS3L2 exoribonuclease safeguards endoplasmic reticulum-targeted mRNA translation and calcium ion homeostasis. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2619. PMID: 32457326. PMC7250864.