HIV-1
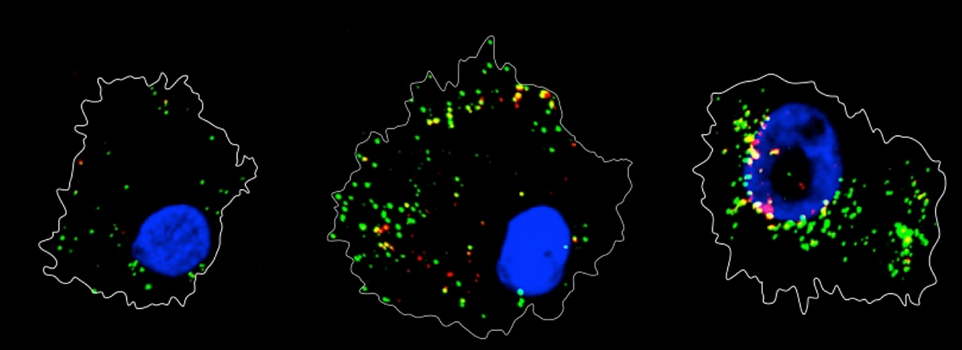
How HIV-1 overcomes our defenses and infects our cells has been studied intensively for over 30 years. While much has been learned, there remain events in the viral life cycle that resist interrogation. One such area is the initial intra-nuclear portion of infection, from the virus’s nuclear entry to its integration into chromatin.
Our Research
An image-based method would be useful for investigating this phase, and so we developed a highly specific and sensitive imaging assay, ViewHIV, for directly visualizing the early phases of HIV-1 replication, a portion of the viral lifecycle which has been resistant to interrogation due to a lack of such approaches. We then went on to use the ViewHIV methodology to determine that the HIV-1 viral capsid protein (CA) enters the nucleus and associates with HIV-1 genomic DNA in both transformed and primary cells. We also find that CA’s interaction with the host polyadenylation factor, CPSF6, enhances viral nuclear entry and potentiates HIV-1’s depth of nuclear invasion, potentially aiding the virus’ integration into gene dense regions.
Our Results
The genome wide RNAi screen we completed to identify HIV-1 dependency factors (HDFs) found multiple previously unappreciated proteins which have roles in HIV-1 replication including the nuclear importer, TNPO3, and the nuclear pore complex proteins NUP358 and NUP153, which help HIV-1 enter the host cell’s nucleus. This was the first whole genome siRNA screen done for a pathogenic human virus and included a strategy to find host factors which impact both early and late phases of infection.
In a subsequent more intensive screening effort we used multiple orthologous RNAi reagents (MORR) to find HDFs discovered a role for the host factor, BRD4, in HIV-1 latency and as a negative regulator of viral replication. Antagonism of BRD4, via RNAi or with a small molecule inhibitor, JQ1, both increased proviral transcriptional elongation and alleviated HIV-1 latency in cell-line models. In multiple instances, JQ1, when used in combination with the NF-κB activators Prostratin or PHA, enhanced the in vitro reactivation of latent HIV-1 in primary T cells.
Let's have the next big breakthrough together!
