TEAM CGM: Team Support to Improve Glycemic Control Using CGM in Diverse Populations
Purpose
To evaluate if continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) can improve glycemic control in the primary care setting targeting individuals with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes.
Aims:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of pharmacist supported CGM in the primary care setting.
- Evaluate CHW support beyond pharmacist + CGM.
- Evaluate Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance (RE-AIM) framework.
- Determine total cost and cost-effectiveness of CGM and the supportive components (e.g., clinical pharmacist and CHW) from the perspective of the healthcare organization.
Study Design
A Sequential, Multiple Assignment, Randomized Trial (SMART). Enrolled patients are first randomized to receive CGM with clinical pharmacist support vs. pharmacist support only. After 6 months, hemoglobin A1c is assessed. Those in both groups not meeting goals in therapy receive additional support. Besides clinical pharmacist support, patients can also receive assistance from a Community Health Worker (CHW).
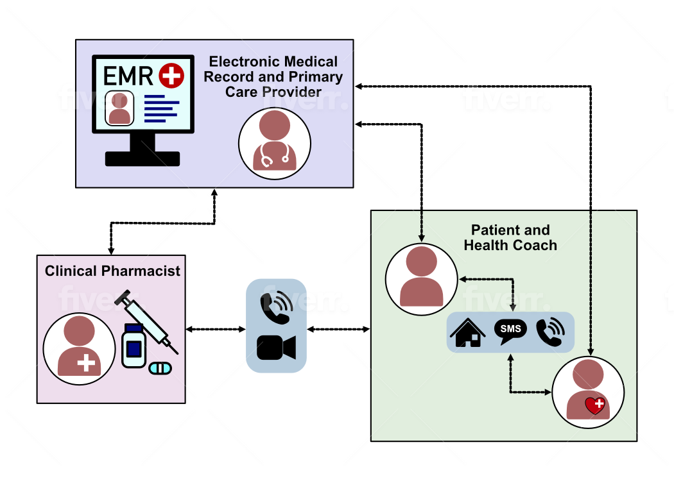
Study Enrollment
Adult patients (age 18+) are identified from registries or the electronic medical record, having a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and elevated hemoglobin A1c level.
Participating Sites:
Study Timeline
A 5-year NIH grant proposal was funded April 2023 (ending 2028). A pilot study of up to 10 participants is expected to begin early 2024. The randomized trial would begin Spring, 2024.
Project team:
Karen Clements, MPH, ScD
Cecilia Davis
Jessica Wijesundara, MPH, CHES
Emmanuella Demosthenes, BS

Diana Rinker, M.Ed.Psy

Zak Dabbagh, BS




